Step-by-Step Guide: React SSR with Spring Boot and GraalVM
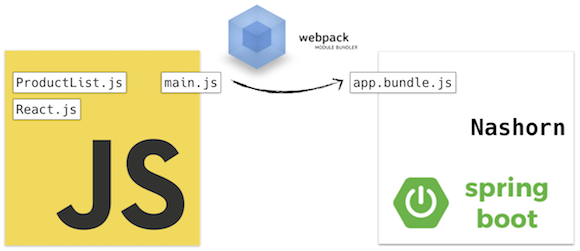
This guide explains how to implement server-side rendering (SSR) for a React application using Spring Boot and GraalVM.
1. Project Structure
The project has a simple layout:
ssr-springboot-react-graalvm/
├── frontend/ ← React app
├── src/ ← Spring Boot backend
├── pom.xml
└── ...2. Clone and Install Prerequisites
Ensure you have Java, Maven, Node.js, and npm installed. Then:
git clone https://github.com/jenylion/ssr-springboot-react-graalvm.git
cd ssr-springboot-react-graalvm3. Install Frontend Dependencies
cd frontend
npm install
npm run buildThis builds the React app and outputs it to frontend/build.
4. Start the Spring Boot App
In the project root, run:
./mvnw spring-boot:runOr if using Windows CMD/PowerShell:
mvn spring-boot:run5. Call the SSR Endpoint
You can now call the SSR endpoint from a browser or using curl:
curl "http://localhost:8080/render?component=App&props=%7B%22name%22%3A%22Ahmad%22%7D"6. How It Works
The backend loads frontend/build/static/js/main.js using GraalVM’s JavaScript engine. The bundled JS must export a renderComponent function like this:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOMServer from 'react-dom/server';
import App from './App';
export function renderComponent(componentName, propsJson) {
const props = JSON.parse(propsJson);
switch (componentName) {
case 'App':
return ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<App {...props} />);
default:
throw new Error("Unknown component: " + componentName);
}
}7. Controller and Service (Java)
The Spring Boot service loads and evaluates the JS using GraalVM:
public String renderComponent(String componentName, String propsJson) throws Exception {
String path = "frontend/build/static/js/main.js";
String jsCode = Files.readString(Paths.get(path));
try (Context context = Context.newBuilder("js")
.allowAllAccess(true)
.option("js.ecmascript-version", "2022")
.build()) {
context.eval("js", jsCode);
Value renderFn = context.getBindings("js").getMember("renderComponent");
return renderFn.execute(componentName, propsJson).asString();
}
}Summary
This setup enables React components to be rendered server-side from Java using GraalVM, improving SEO and initial load times. The frontend lives inside the backend project, and no copying is needed after npm run build.
Related Article
Advanced SSR and SSG with Spring Boot & React

There are 2 comments
git repository
Hi Ahmad, Nice article, Do you have git respository for the example you have provided in the blog. thanks, Johnson
Now in Github
Hi Johnson I just did and created a repo in Github . Enjoy hacking